Acne Treatment in Gurgaon

How Does Acne Happen ?
Acne develops through the following process:
1. Sebum Production
2. Clogged Pores
3. Bacterial Growth
4. Inflammation
Triggering Causes
Several factors can trigger or worsen acne:
1. Hormonal Changes
2. Diet
3. Stress
4. Medications
5. Cosmetics
6. Friction or Pressure on Skin
Items like telephones, helmets, tight collars, and backpacks can irritate the skin and promote acne.
7. Genetics
How to Prevent Acne?
Preventing acne involves several strategies to keep pores clear and reduce inflammation:
1. Skincare Routine
Cleanse: Wash your face twice a day with a gentle cleanser to remove excess oil and dead skin cells.
Exfoliate: Use a gentle exfoliant to remove dead skin cells, but avoid over-exfoliation, which can irritate the skin.
Moisturize: Use a non-comedogenic (won’t clog pores) moisturizer to keep skin hydrated.
Consult Dr.Geeta Grewal for a skin care routine based on the cause of your acne
2. Avoid Touching Your Face
Touching your face can transfer oils and bacteria from your hands to your skin.
3. Choose Non-Comedogenic Products
4. Maintain a Healthy Diet
5. Manage Stress
6. Limit Sun Exposure
7. Avoid Heavy or Tight Clothing
8. Consult a Doctor
Acne Treatment
It is common to experience acne. Mostly, teenagers and adults till a certain age struggle with it. It can be occasional breakouts or chronic acne; it affects both confidence and comfort. And if you live in a busy city like Gurgaon, it becomes even more common to experience acne.
At 9Muses Wellness Clinic, we offer advanced acne treatment in Gurgaon tailored to your skin type and acne severity.
We start by analyzing the skin deeply to understand the root cause of the acne. It can be due to hormonal imbalances, bacterial infections, or lifestyle-related factors.
After identifying it, our experts create a personalized treatment plan that is the best for your skin. It may include medical-grade facials, chemical peels, oral or topical medications, and laser sessions.
At our clinic, we focus on long-term results. That is why we don’t just treat the surface but also prevent future breakouts.
Our treatments are designed to minimize inflammation, unclog pores, and improve skin texture without harsh side effects. Located in the heart of Gurgaon, we combine medical expertise with modern technology to deliver visible improvements.
So, if you are someone looking for safe, effective, and scientifically backed acne treatment in Gurgaon, then book your consultation now!
Acne Treatment Cost in Gurgaon
There are a few factors that affect the acne treatment cost in Gurgaon. How much you will have to pay varies based on the type of treatment recommended, the severity of acne, and the number of sessions required.
However, at 9Muses Wellness Clinic, we customize our prices after a thorough consultation. Whether your skin requires a facial, laser or medical treatments, we provide transparent pricing with no hidden charges.
Book your consultation to get a personalised cost estimate.
Acne Doctor Treatment in Gurgaon
Acne can go wrong if not treated in a timely manner. It is a common problem, and all of us make our assumptions, and this is what sometimes makes it worse.
Consulting a qualified specialist is your only option if your acne is not going away for a long time. A dermatologist can help you get rid of your acne medically.
At 9Muses Wellness Clinic, you can contact an expert-led acne doctor for treatment in Gurgaon. They understand your unique skin needs and plan the treatment accordingly.
The clinic is led by Dr. Geeta Grewal, Celebrity Cosmetologist. She brings years of clinical experience and follows a medical-grade approach to treating acne safely and effectively.
In each of the consultations, we perform a thorough examination to identify the root cause of your acne. This is what helps your acne doctor to design a treatment plan that best suits you.
Here are the key benefits of choosing an acne doctor:
- It helps you ensure you get a precise diagnosis.
- You get professional guidance instead of over-the-counter trial and error.
If you are in search of a trusted acne specialist in Gurgaon, then 9Muses Wellness Clinic is your way to go. Book your consultation now!
Acne Arrest Facial in Gurgaon
Acne arrest facial in Gurgaon is a go-to solution for people who are battling with frequent breakouts or dull, acne-prone skin. This is one of the targeted, and result-oriented solutions to this cause.
This treatment is designed to deeply cleanse, soothe inflammation, and prevent further acne formation. And the best part is it is suitable for both teens and adults seeking clear skin.
Here is what this facial does to your skin:
- Deep pore cleansing to remove excess oil, dirt, and impurities.
- Gentle exfoliation to slough off dead skin cells and unclog pores.
- Anti-bacterial treatment to reduce acne-causing bacteria
- Calming mask and serums to soothe redness and irritation
To people who suffer from mild to moderate acne, acne arrest facials have shown effective results. It also helps in reducing the frequency of breakouts.
If you take regular sessions, it also helps you promote a more balanced skin tone, smoother texture, and reduced acne scars over time.
Here is why most people choose this:
- This facial combines advanced skincare products with the latest techniques.
- It is non-invasive.
- It is suitable for most skin types and requires minimal downtime.
- It is a safe and effective option to include in your long-term skincare routine.
At our clinic, we customise every acne arrest facial in Gurgaon based on our client’s skin condition.
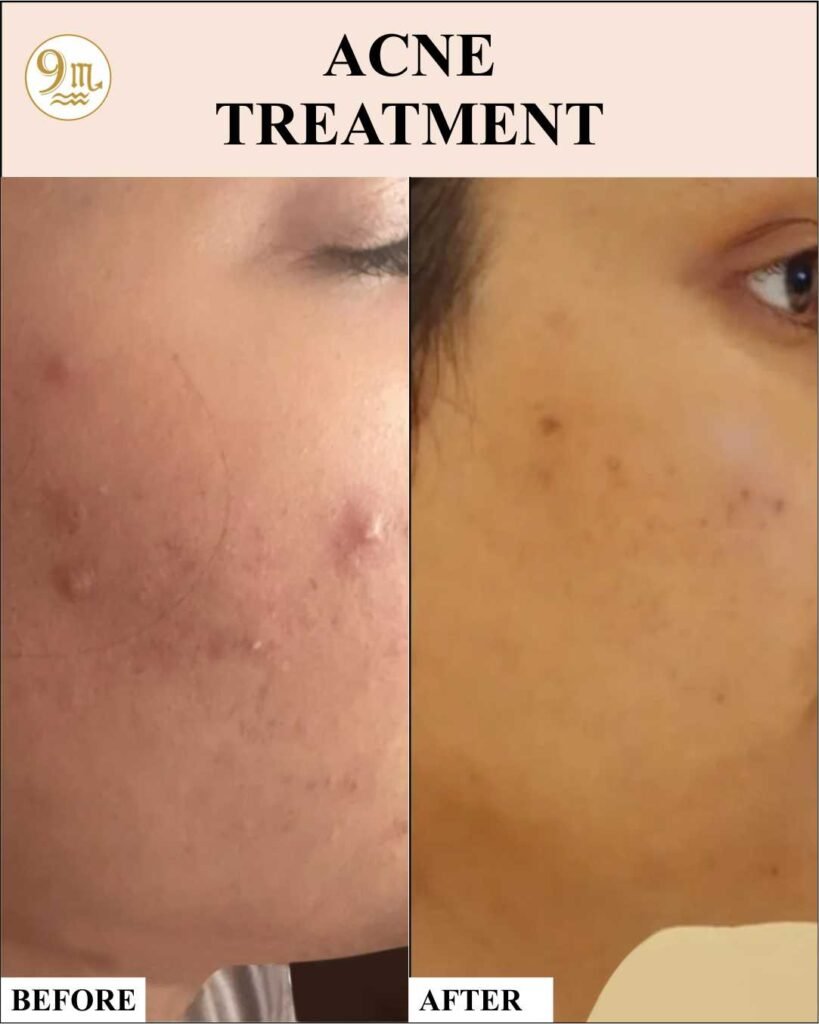
Before And After

Frequently Asked Questions
Treatments for Acne
When combined with other treatment it bring amazing results and treats the problem to the root.
Consult and Aesthetic Doctor today.
Laser Therapy: Targets deeper skin layers to kill acne-causing bacteria and reduce inflammation, promoting clearer skin.
Several types of laser therapies are used to treat acne, each with specific benefits and suitability for different skin types and acne severities:
1. Blue Light Therapy
- Mechanism: Targets and kills P. acnes bacteria.
- Best for: Mild to moderate acne.
- Benefits: Reduces inflammation, minimal side effects, non-invasive.
2. Diode Laser
- Mechanism: Penetrates deep into the skin to target sebaceous glands.
- Best for: Moderate to severe acne.
- Benefits: Reduces oil production, effective for treating cystic acne.
3. Fractional Laser
- Mechanism: Creates micro-injuries to stimulate collagen production and skin renewal.
- Best for: Acne scars and overall skin texture improvement.
- Benefits: Promotes collagen production, reduces acne scars, improves skin texture.
4. Nd:YAG Laser
- Mechanism: Penetrates deeply to target sebaceous glands and blood vessels.
- Best for: Deep acne lesions and scars.
- Benefits: Reduces active acne, minimizes scarring, suitable for deeper skin issues.
How Microneedling Works for Acne
Microneedling, also known as collagen induction therapy, is a minimally invasive cosmetic procedure that involves using a device with fine needles to create tiny punctures in the skin. These micro-injuries trigger the body’s natural healing process, which stimulates collagen and elastin production. Here’s how microneedling helps with acne and acne scars:
Microneedling can be an effective treatment for improving the appearance of acne scars and overall skin texture. When performed by a skilled professional and tailored to individual skin types, it can yield significant benefits with minimal risk.
Blue Light Therapy: Uses specific light wavelengths to effectively treat active acne. Blue light therapy treats acne by killing bacteria, reducing inflammation, and preventing breakouts. It’s non-invasive, with minimal side effects and no downtime.
Blue light therapy can be an effective and gentle treatment for acne across various skin types, offering a non-invasive option to reduce bacterial growth and manage breakouts.
Book an appointment